KEY TAKEAWAYS
Companies that have adopted Agile principles are delivering better customer experience than companies that have continued to use traditional project management methods. The 2018 Standish Group report mentioned that success rates of Agile projects were two times higher and one-third less likely to fail than projects guided by traditional PM. Based on Agile values and principles, companies chose methodologies like Kanban and Scrum to ensure that their projects will result to the right products or services that deliver perceived value to users.
Why Is Choosing between Kanban vs. Scrum Important?
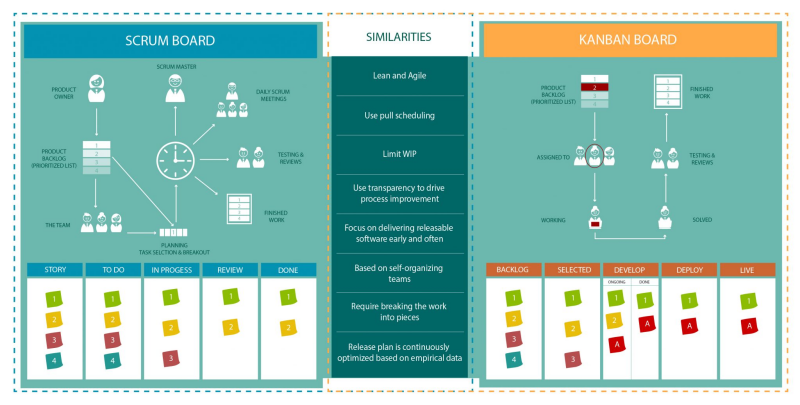
Agile project management methodologies such as Kanban and Scrum provides several benefits to the project team, regardless of which you choose. Both methodologies enable teams to:
- Build products or services with superior quality
- Satisfy customers
- Have better control over the project
- Increase project visibility and improve predictability
- Reduce risks
But when is it more advantageous for a project, team, or organization to use Kanban vs. when to use Scrum? Although both methodologies adhere to Agile values and principles, they are not interchangeable. Each has a different focus and set of practices.
READ ALSO: Agile vs. Waterfall: Differences in Software Development Methodologies?
What Is Kanban?
Kanban is an Agile methodology based on a lean manufacturing method used by Japanese automotive company Toyota. Kanban uses a visual system that enables project teams to manage work by balancing demands with capacity. Visualization helps the team monitor the progress of activity and the execution of the process from start to finish. Teams can quickly identify bottlenecks in the workflow, so they can make better decisions in how much limit they can put to the number of work in progress (WIP).
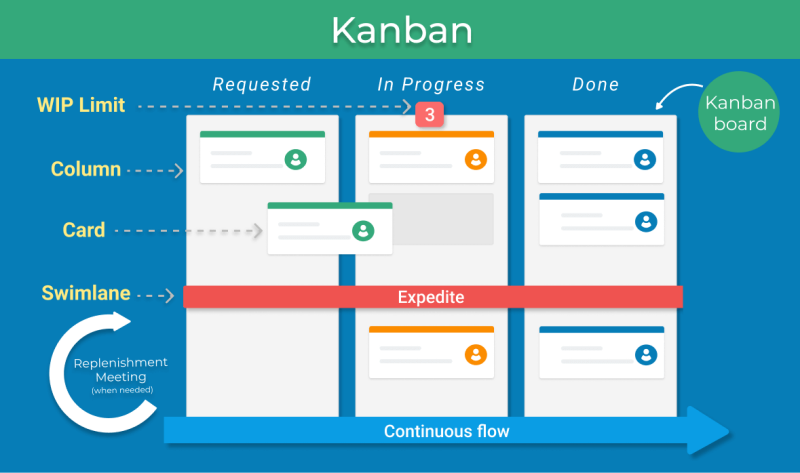
Aside from workflow visualization and WIP limits, other guiding principles include documenting the policies (defining ‘done’), managing the workflow, implementing feedback loops, and improving continuously. In Kanban, teams measure the following:
- Team velocity – how many tasks a team can deliver in a period of time
- Lead time – the average time a client has to wait for the team to complete its request, starting from getting a client request.
- Cycle time – the average time a team completes a request, starting from working on the request.
Teams use the Kanban methodology in software development projects, process improvement, sales management and distribution, customer support organization, and leads management.
READ MORE: Best Kanban Board Software & Tools
What Is Scrum?
Scrum is an Agile methodology that provides an alternative framework to traditional sequential approach. It is an iterative and incremental approach where a team of 10 or fewer members break complex project goals into smaller goals and complete them in time-boxed periods of two to four weeks called sprints. The creators of Scrum borrowed the term from rugby, which describes the formation of players to emphasize teamwork in the methodology. The Scrum team identifies specific roles, artifacts, and ceremonies in its practice:
- Owner – represents the customer, manages the backlog, and helps prioritize work
- Scrum Master – enables the Scrum team to work smoothly according to Agile principles
- Scrum team – self-organizing team that chooses and completes work items
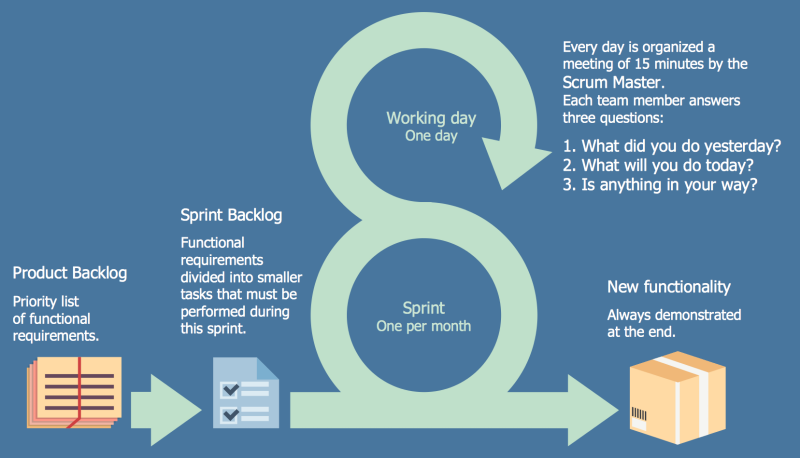
Scrum teams hold sprint planning to decide what to work on the next sprint and daily stand-ups (scrums) to get the latest work updates from every team member. At the end of every sprint, the team conducts a sprint review to review the work, demonstrate the completed work, and collaborate with stakeholders to know what to work on next. They also conduct a sprint retrospective to reflect on the past sprint and identify areas for continuous improvement. Scrum teams mainly measure velocity in story points to help them understand how much work they are capable of in a given sprint. Industries that use Scrum include teams in software development, financial services, pharmaceuticals, telecommunications, and education, among others.
ALSO READ: The Beginner’s Guide to Scrum and Agile Project Management
Kanban vs. Scrum: What Are the Differences?
Kanban and Scrum are two of the top project management methodologies available and can help a project team reach its goals in a more organized and flexible way and deliver products or services that will satisfy customers. But which one will suit a type of project or team better?
By project type
Kanban focuses on workflow, but a team’s workflow can change at any time. Teams can add new tasks or cards for small fixes or enhancements in the backlog and remove blocked tasks. They can change priorities and WIP limits if their capacity for work changes to accommodate changed demands.
Scrum suits time-sensitive projects because of its defined sprints. It does not allow changes to the project scope or addition of new tasks during a live, ongoing sprint. So it is ideal for projects with specific features or milestones for a planned release or launch.
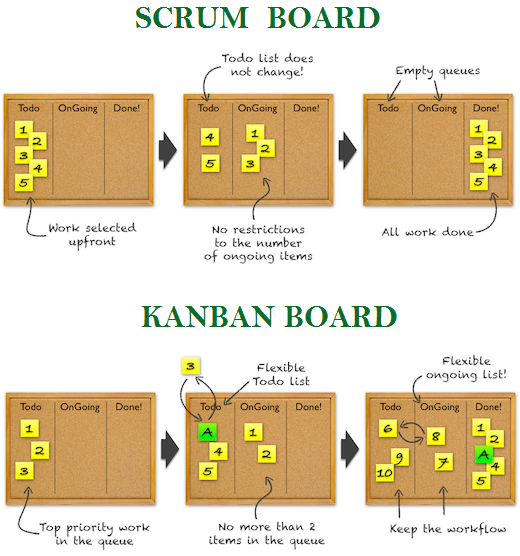
By team type
Kanban’s team selection is specialized for the kind of work requests they will handle. It does not specify roles and leaves it to the existing organization. The methodology also does not describe any specific rules how to conduct the workflow except for defining policies in how a task flows from one column to the next. WIP limits the number of tasks, while lead and cycle times measure team performance
Scrum teams have specific roles. It also describe rules, practices or ceremonies, outputs or artifacts, and when to hold or produce them. Sprints have defined periods, prioritization is by story points, and teams have daily meetings. Sprints limit the number of defined tasks, while velocity and burndown charts measure team performance.
READ MORE: What is Project Management? Definition, Types & Examples
Kanban and Scrum?
Kanban and Scrum are methods that help teams manage and deliver projects. They are tools that enable teams be more successful. As projects become more complicated, teams will need better tools that they can customize to help them achieve success. They can take the most advantageous qualities of any methodology and combine them to create a hybrid approach that is sensible for both the project requirements and team workflow. For example, Kanban teams can incorporate planning and reviews, while Scrum teams can use WIP to manage their workflows.