Key takeaways
Every project team needs a decision-making framework to meet its objectives and reduce floundering. One such tool is DACI.
The DACI decision-making framework offers project managers a structured method for distributing roles and responsibilities. Decision-making is a crucial and ongoing part of the project lifecycle, and DACI helps teams avoid confusion, reduce delays, and improve accountability. A DACI chart offers teams visibility into how stakeholders influence projects or decisions, from organizational leaders to team members and clients.
Read on to learn what DACI is and how to adopt the decision-making framework for your team.
What Is DACI?
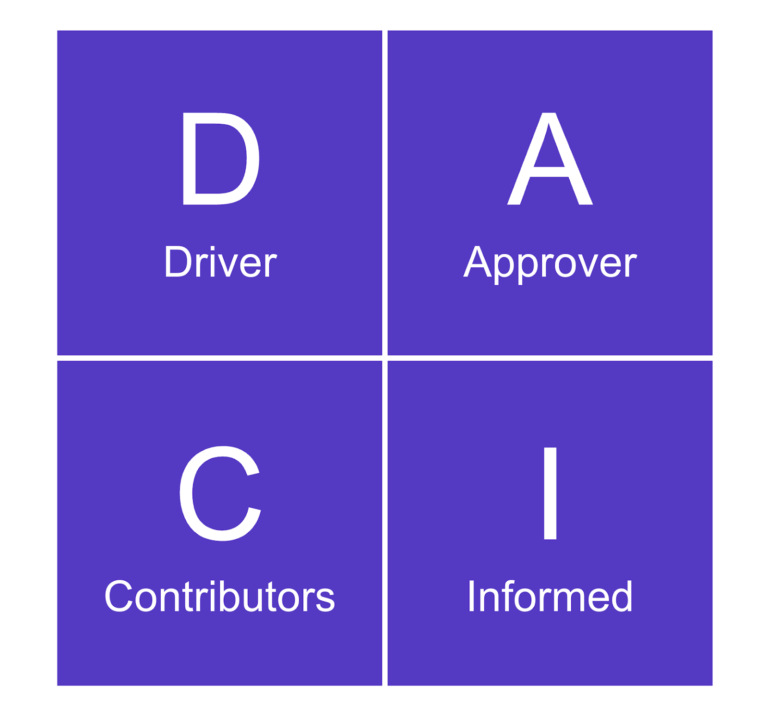
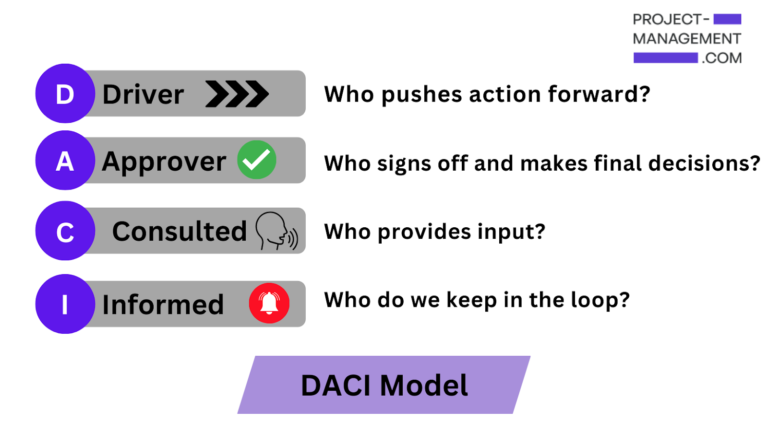
DACI is a framework that defines the roles and responsibilities of stakeholders for a project team. DACI is also an acronym for the four roles — Driver, Approver, Contributor, and Informed — each representing an essential part of the project life cycle.
DACI allows project managers to divide project stakeholders into clear roles that influence project tasks and results. This structured approach provides clearly defined expectations for individual project stakeholders that enable communication, collaboration, and confidence in completing project deliverables.
Within project management terminology, DACI is an example of a responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) and is closely related to a RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed).
Roles in the DACI Model
DACI stands for Driver, Approver, Contributor, and Informed. Together, the stakeholders within the DACI chart can ensure efficient, transparent decisions. While organizations may adjust responsibilities for each stakeholder group, they generally share the following vocations.
| Driver | Drives decision-making and deliverables on behalf of stakeholders. |
| Approver | Makes the final call approving a decision or deliverable. |
| Contributor | Provides input and direct assistance in the decision or deliverable. |
| Informed | Kept aware of progress but not directly involved in the decision or deliverable. |
Here’s an in-depth breakdown of each role within the DACI chart, with definitions of project management terms that you need to remember to better understand the importance of the framework.
Driver
The Driver role is typically the team leader or project manager. A special case where multiple Drivers may be necessary is managing different components of large or complicated projects; however, this can also complicate team processes. In either case, the Driver is accountable for overseeing an entire project’s lifecycle from inception to completion.
Some of the Driver’s core responsibilities include:
- Establishing and ensuring project deliverables
- Assigning individual tasks and activities
- Setting goals, project milestones, and deadlines
- Organizing and running meetings
- Maintaining project documentation
It’s ultimately up to the Driver to direct the project’s trajectory and ensure success for everyone involved. The Driver’s success hinges on the supporting roles in the DACI framework and the productivity of the project’s team members.
Approver
The Approver has the final say on every detail of the project or task. Much like the Driver, some teams utilize multiple Approvers, but these examples are vulnerable to over-complicated workflows. For the sake of simplicity and the DACI model, it’s best to stick with a single Approver.
Regardless of the project size, the Approver plays a vital role in the project lifecycle. Rather than playing a hands-on role, Approvers offer a non-biased, objective approach to project tasks and decisions. As the Driver presents decisions for consideration, the Approver provides much-needed clarity for teams and ensures decisions align with business objectives.
Also read: What is Stakeholder Analysis? Definition & Examples
Contributor
Contributors are stakeholders that inform the decision-making process based on their knowledge or hands-on experience during the project. Specifically chosen by the project driver, Contributors typically account for most individuals within a DACI matrix.
Examples of Contributors on a project team include:
- Business and data analysts
- Industry and subject matter experts
- Product designers and engineers
- Customer support and sales representatives
- Product or service client
- Business owners and investors
Because of their unique perspectives, Contributors are a valuable part of the decision-making process. Their knowledge and expertise generally serve as a launchpad for the entire project lifecycle, and they often significantly influence the final, most important decisions.
Informed
While the first three roles of the DACI model are stakeholders with significant involvement in a project, the Informed role includes individuals with no direct authority or association with the decision-making process.
While they may not be directly involved, the Informed often must keep track of project progress. Whether it’s an employee from an adjacent department or the client receiving the final deliverable, DACI offers visibility and ensures transparency for Informed stakeholders. Clients can sometimes directly impact day-to-day responsibilities, especially when using an iterative project management methodology that dictates regular engagement between the client and the team to ensure deliverables meet customer needs.
Read more: Waterfall Model Methodology: Everything You Need to Know
When to Use DACI in Project Management
The best time to create a DACI chart is after the project charter is approved and before the project kickoff meeting. During the planning phase of the project management lifecycle, project leaders can estimate project needs, identify stakeholders, and develop a DACI that breaks down expected roles and responsibilities.
DACI or a similar responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) is a crucial part of any resource management plan and ensures a structured process for decision-making. During the project kickoff meeting, project managers can present a DACI for discussion, collect feedback, and make adjustments before project work begins. In addition to its planning value, a DACI chart is a visible reminder for new and existing stakeholders throughout the project’s remaining life.
How to Use DACI in Project Management
DACI is a general framework that is widely applicable across different industries and functional teams. With a project charter presenting objectives that include one or multiple decisions and deliverables, a DACI chart can organize the project team and workflows.
During the resource and stakeholder management planning phase, project managers can estimate who and what is necessary to complete the project. With the needed resources in mind, the project manager places stakeholders in their respective quadrants of the DACI framework.
Once established, the DACI chart is reusable for similar tasks during the course of the project. As project managers know, there’s no right or wrong way to implement DACI if the result is improved structure, productivity, and accountability.
Examples of DACI
One example of DACI in action is a software development team developing and releasing a new application to a client. In this scenario, roles could be split as follows:
| Driver: The product owner is responsible for overseeing the project, including gathering input from contributors and maintaining the project schedule. | Approver: The chief technology officer (CTO) or chief product officer (CPO) is responsible for approving the release of the software application. |
| Contributors: The software development team is responsible for designing, building, testing, and deploying versions of the application before releasing it to clients. | Informed: The client and customer support team who will be using and supporting the software once deployed need to be abreast of the product’s progress and specifications. |
Another example of DACI is a restaurant determining a new seasonal menu. Unlike the previous example, which could support multiple decisions throughout an iterative project life cycle, this scenario focuses on a single decision.
| Driver: The head chef is responsible for overseeing the decision by coordinating input from stakeholders and presenting a final proposal to the approver. | Approver: The restaurant CEO has the final say on the seasonal menu, ensuring menu items meet are feasible and aligned with organization budget and culture. |
| Contributors: The marketing team can offer insights into food and market trends, and the kitchen staff can brainstorm, prepare, and taste test potential recipes. | Informed: Restaurant managers and staff need to be aware of the new menu as they will be serving the food, and customers need to know about the menu so they can get their reservation. |
The last example of DACI offers a different perspective of responsibility assignment information by using a chart. Rather than a quadrant that limits information to a single process, a DACI chart allows for plotting multiple processes and role assignments. The chart below shows the various processes of a team that manages a cybersecurity news website. Each person for each process has a letter representing the four roles of DACI.
| Project Manager | Content Director | Expert Writer | Graphic Design | Website Developer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily standup meeting | D | A | C | C | C |
| Write new blog on malware | A | – | D | I | I |
| Send subscriber newsletter | D | A | C | C | I |
| Update WordPress templates | D | A | I | I | C |
| Redesign website logo | D | A | – | C | I |
Also read: Top Reasons Why Projects Fail & Solutions for Them
Benefits of Implementing the DACI Framework
The DACI framework offers multiple benefits to teams looking to bring structure to responsibility assignment and decision-making. These benefits include clearly defined roles and responsibilities, streamlined collaboration, accountability, risk management, adaptability, and recyclability.
Clear roles and responsibilities
Foremost, a DACI chart organizes stakeholders into defined roles and responsibilities. These roles are visible reminders for the project manager and team and a roadmap for a specific task or decision.
Streamlined collaboration
DACI charts also provide teams with a clear structure that streamlines stakeholder collaboration. Without a guiding structure, teams can flounder in the face of making decisions, while a DACI ensures stakeholders know their part and who’s responsible for the next steps.
Accountability and risk management
By adopting DACI, teams establish an additional layer of accountability, risk management, and quality control. Whether it’s a deliverable for a client or an internal milestone, DACI offers a structured process that engages stakeholders and optimizes project management results.
Adaptable and reusable
A DACI is a flexible and reusable tool across teams with similar projects or functions. While stakeholders can change during a project, a DACI offers consistency for continued project progress. Not just reusable for a single project, DACI charts are organizational assets that allow PMOs and other teams a tool they can amend and reuse for different projects.
Read more: 20 Key Project Management Questions to Ask for Project Success
FAQs
Bottom Line: Decision-Making with DACI
The DACI framework offers a standardized and structured approach that enables project management. While teams of varying sizes can struggle to make decisions or take action on project tasks, a DACI helps clarify roles and responsibilities for every stakeholder. Implementing DACI facilitates increased visibility and accountability within key decision-making processes. When implemented by a skilled project manager, DACI establishes greater levels of communication, collaboration, efficiency, and, as a result, project success.