KEY TAKEAWAYS
A work breakdown structure (WBS) is a project management technique that organizes complex projects into manageable tasks, using a visual and hierarchical format to enhance efficiency. It helps to define the scope of work, allocate resources effectively, and track progress towards each milestone and deliverable. By utilizing a WBS, project managers can ensure that all necessary tasks are identified and completed in a timely manner, ultimately driving project success.
To complete a project, it is essential to have a clear understanding of the milestones, deliverables, and tasks that need to be accomplished. These components of project management are the building blocks of a successful execution. Without a comprehensive project management plan in place, monitoring progress and ensuring timely completion becomes a challenge. This is where a work breakdown structure becomes crucial.
Key Considerations When Creating a Work Breakdown Structure
Project details
Before creating a WBS, it is important to have a comprehensive understanding of the project. This entails knowing the project objectives, scope, and requirements so the project manager can accurately identify and define the deliverables that need to be included.
A WBS is typically delivery-oriented, meaning it focuses on the final outcomes or products that need to be delivered to meet the project’s objectives. It shows three levels of information:
- Level 1: Project title of final deliverable (parent task/project objective)
- Level 2: Major dependencies of the final deliverable
- Level 3: Tasks to complete the major deliverables
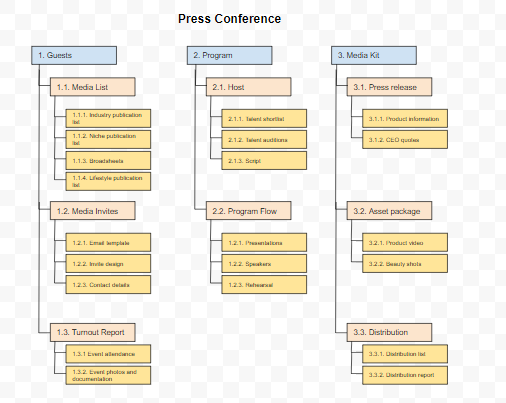
For example, imagine that you work for a press agency and you’re tasked to organize a press conference for your client’s product launch. Here are some deliverables you might need to provide:

Work breakdown structure types
There are two main types of WBS: deliverable-based and phase-based. The choice between these two types depends on the nature of the industry and project at hand.
In a deliverable-based WBS, the focus is on breaking down the project into smaller, manageable deliverables. This approach is useful when the project involves creating specific outcomes or products.
A phase-based WBS, on the other hand, divides the project into different phases or stages. This type of structure is more suitable for projects that involve processes that follow a linear approach.
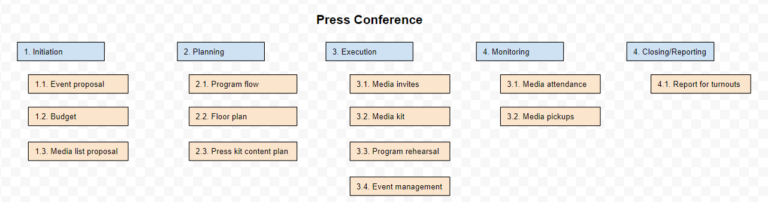
The image above illustrates how the press conference WBS would look like if it were phase-based. Instead of the major deliverables at level 1, they’re replaced by the phases of the project. Level 2 is composed of the deliverables that need to be submitted per phase.
Work breakdown structure formats
Several formats can be used to effectively organize and present the information when creating a work breakdown structure.
One commonly used format and the simplest to do is the outline structure. It represents deliverable hierarchies through indents and numbering. If your level 2 deliverable is numbered as 1, then the level 3 deliverables under it will be labeled 1.1, 1.2, 1.3,and so on. Here’s an example:

Another format is the tabular structure, which presents the information in a table format. The leftmost column will contain the major deliverables. The succeeding columns after that will house the next deliverable levels.
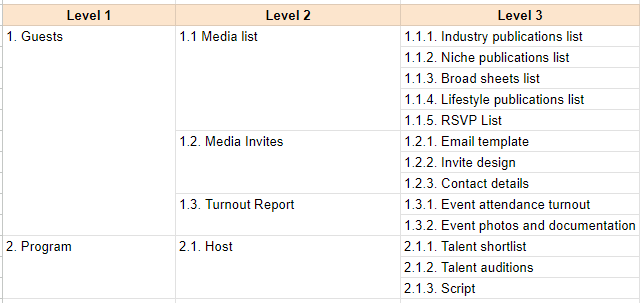
The hierarchical WBS is also shown in a tabular form. The difference lies in how the information is organized.
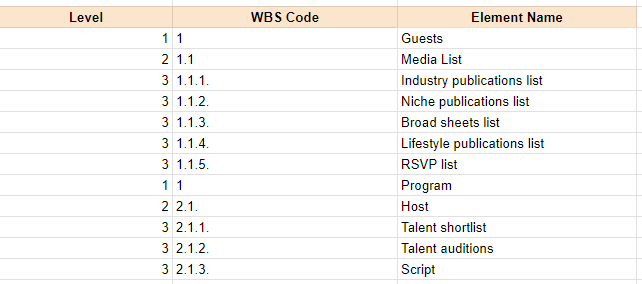
Finally, the tree structure, which is similar to the outline format but visually represents the relationships between tasks using branches and nodes.
Choosing the right format for your WBS depends on the complexity and nature of your project, your personal preference, and the needs of your team.
How to Create a WBS
1. Define project and boundaries
In creating a work breakdown structure, first you must define the project and its boundaries. This requires going through the necessary documents and connecting with relevant stakeholders to gain a clear understanding of the project objectives and key expectations. By doing so, you can establish a solid foundation for the WBS, ensuring that all tasks and deliverables are aligned with the overall project goals.
For example, if you’re going to organize a press conference, you’ll need to understand what it is for, how many attendees you’re targeting, what type of publications you need to invite, your client’s budget, and what materials your client is willing to provide for the press.
2. Identify elements and deliverables
Once you have a clear understanding of the objectives of your project, it is time to identify the deliverables that need to be submitted in order to achieve those objectives. These deliverables are the tangible outcomes or results that will be produced as part of the project. They can be documents, reports, prototypes, or similar items that contribute to the successful completion of the project.
In the case of press conferences, deliverables could include a media list, a media kit, a program flow, and a report for the results.
Identifying these deliverables is an important step in developing a work breakdown structure, as it helps to define the specific tasks and activities that need to be carried out. By clearly identifying the deliverables, you can ensure that all necessary components are included in your WBS and that you are able to meet the project’s objectives effectively.
3. Gather stakeholders and team members
The next step is to gather all relevant stakeholders who are involved in the project. This includes all types of stakeholders—individuals or groups—who have a vested interest in the project’s success and those who will be directly impacted by its outcomes.
By involving these stakeholders from the beginning, their input and expertise can be leveraged to ensure that the project is aligned with their needs and expectations. It would also be good to request for their approval for the outlined deliverables. This step ensures that all parties involved are in agreement and provides a formal endorsement of the project plan.
4. Add additional details
Once your work breakdown structure elements and deliverables have been approved, you can proceed with adding more details to ensure a smooth and successful project execution. This involves assigning specific tasks to individuals, setting due dates for completion, and determining the budgetary requirements, among others.
Including these additional details helps you effectively communicate expectations to your team and stakeholders, ensuring that everyone is on the same page and working towards a common goal.
Furthermore, seeking another round of approval from your stakeholders or simply communicating progress can provide reassurance and validation that your plans are aligned with their expectations. Going through this process minimizes any potential risks or misunderstandings and increases the likelihood of project success.
5. Create the WBS dictionary
After your work breakdown structure is approved, you can start creating a WBS dictionary. The WBS dictionary provides detailed information about each element in the WBS, including its description, deliverables, responsible parties, and other relevant information.
This document acts as a reference guide for the project team and stakeholders to ensure that everyone has a clear understanding of the scope and objectives of each work package. It also helps in managing the project by providing a baseline for measuring progress and tracking dependencies between different elements of the WBS. By creating a comprehensive WBS dictionary, you can enhance communication, improve project planning, and facilitate effective project execution.
When to Use a Work Breakdown Structure
A work breakdown structure provides a structured framework for organizing and planning tasks. However, it is important to recognize that it is not always necessary.
One scenario where a WBS becomes essential is when the project scope is not clearly defined. In such cases, a WBS can help push the team to identify and define the scope, ensuring that all necessary tasks are accounted for. Additionally, complex projects with multiple deliverables and dependencies can greatly benefit from a WBS, as it offers a visual representation that aids in aligning and focusing the team’s efforts.
For small and straightforward projects, however, a WBS can be an unnecessary burden. These types of projects usually have a clear and concise scope from the start, so it is easy to directly assign tasks even without a detailed breakdown structure.
Similarly, repetitive and routinary projects may not require a WBS as well. In these cases, it is more efficient to rely on standard operating procedures (SOPs) that contain step-by-step instructions for completing the tasks. SOPs help streamline processes and minimize unnecessary documentation, saving time and resources.
WBS Pros
WBS Cons
Frequently Asked Questions
Best Project Management Software for Creating a WBS
ClickUp
ClickUp stands out among other tools when it comes to creating work breakdown structures due to its extensive range of data viewing options. With ClickUp, users can choose from various views to organize and analyze their data effectively.
The doc view allows you to create an outline-type WBS, making it easy to structure and outline tasks and subtasks. The regular list view provides a table that allows you to add more information and elements. For those who prefer visual representations, the whiteboard view proves useful as it allows users to create diagrams for different types of WBS trees. Additionally, ClickUp offers a Gantt chart and other available views to cater to the diverse preferences of teams.
Miro
Miro is a software that excels in providing a team whiteboard, making it ideal for creating tree-like work breakdown structure formats. This tool stands out as the top choice for teams looking for a highly visual approach to designing their WBS. Its core feature lies in its ability to cater to this specific format, allowing teams to easily map out and organize their project tasks in a visually appealing manner.
monday.com
monday.com is a versatile project management tool that offers a high level of customization to meet the unique needs of different projects. Its structure, which resembles a spreadsheet, provides a familiar and intuitive interface for users.
One of the standout features of monday.com is its easy controls for task hierarchies. This means that users can easily organize and structure their tasks into subtasks, allowing for efficient project planning and execution. This feature also enables users to create a WBS effortlessly, which is a crucial component of project management.