Key takeaways
In the project tendering and bidding process, property owners solicit bids from service providers or submit bids to win the right to complete a construction project. A well-organized tendering and bidding process is important for successful project management, as it helps proprietors and organizations find the most qualified service providers for the job at a competitive rate.
In the construction industry, billions of dollars are at stake annually in project bids, highlighting the importance of precision and effectiveness in these processes. Project managers often play a central role in navigating the complexities of bidding and tendering, ensuring each project is awarded to the most capable contractor. Their expertise in finding the best candidate and managing timelines, budgets, and scopes is indispensable.
Read on to learn more about external projects and the intricate bidding and tendering process in construction project management.
What is the bidding and tendering process?
Bidding and tendering in construction project management involves a business or organization inviting third-party contractors to bid for a project. Once an invitation to bid has been tendered, companies can submit a bid indicating their interest in providing their service. Businesses then compare the submitted bids and accompanying proposals against specific criteria to identify the best provider or supplier for the project.
Why is the bidding process important in construction project management?
When an organization lacks the expertise or experience to meet a specific project requirement, it is more cost-effective and time-efficient to seek an outside contractor. In cases like this, the bidding process is essential to ensure that the contract goes to the service provider with the appropriate interests and skills for the job.
For example, a property owner looking to build a chalet will award the contract to the company that has the most experience in building wooden structures. The contractor may also then hire a subcontractor with proven expertise in doing electrical work.
Here are some of the many reasons why bidding is vital in project management:
- Helps businesses find the best and most qualified contractor for the job
- Lays the groundwork for an insightful discussion and sharing of opinions and comparisons on work methods and needs
- Clarifies budget, timing, and scope with third-party input
- Identifies necessary additions or new approaches to completing the project
- Encourages fair competition and transparency among vendors
- Secures high-quality work at the best price
- Builds relationships with new vendors, keeping them on each other’s radar
- Ensures compliance with organizational policies, like requiring multiple bids
- Creates a well-documented contract aligning all parties on responsibilities and deliverables
Guide to an effective contractor prequalification
Pre-qualifying contractors is a crucial step in the bidding process, especially when taking on new work with people you have not worked with before. The prequalification process involves evaluating a contractor’s capabilities, financial stability, and past performance before allowing them to bid on or begin work.
Here are some tips for conducting an effective contractor prequalification.
- Prepare a comprehensive questionnaire. Create or customize a basic prequalification questionnaire to assess contractors based on uniform standards.
- Do background checks. Verify a contractor’s financial health, safety record, and project experience by conducting a background check to rule out those with questionable history.
- Set criteria. To make an informed decision, set clear and consistent criteria for contractor selection, including insurance, licenses, safety records, and communication skills.
- Manage risk. Reduce the risk of hiring unqualified contractors and invite only those who meet your standards.

Public vs private bidding
The bidding process can be either public or private. Let’s look at the key differences between the two.
Public bidding
- Strict legal frameworks govern public bidding processes to maintain fairness and openness.
- The focus on transparency is heightened because public funds, particularly taxpayer money, are involved.
- Public tenders often demand the submission of standardized documents and adherence to specific legal protocols.
- Public bidding encourages fair competition between vendors, providing equal chances for all qualified suppliers.
- This type of bidding facilitates the procurement of high-quality services or goods at competitive prices.
- Public bidding guarantees that contracts are awarded to vendors who meet all qualifications and have the necessary expertise to deliver.
Private bidding
- Private bidding allows for greater flexibility with fewer regulatory obligations and restrictions.
- Innovation and strategic pricing play a more significant role, as vendors often focus on differentiating themselves from competitors.
- Private tenders tend to be less formal and involve shorter, more streamlined documentation compared to public ones.
- Fewer regulatory barriers often lead to a more efficient and faster bidding process.
- Private bidding enables vendors to offer customized solutions and more creative approaches to meet specific client needs.
- Decisions and project implementation are generally quicker, thanks to reduced bureaucracy and a more agile approach.
Types of bids
There are many different types of bids depending on the need and industry. Here are three common types of bids to be aware of if you are a project manager who will be involved in the bidding and tendering process for a project.
Sealed bid
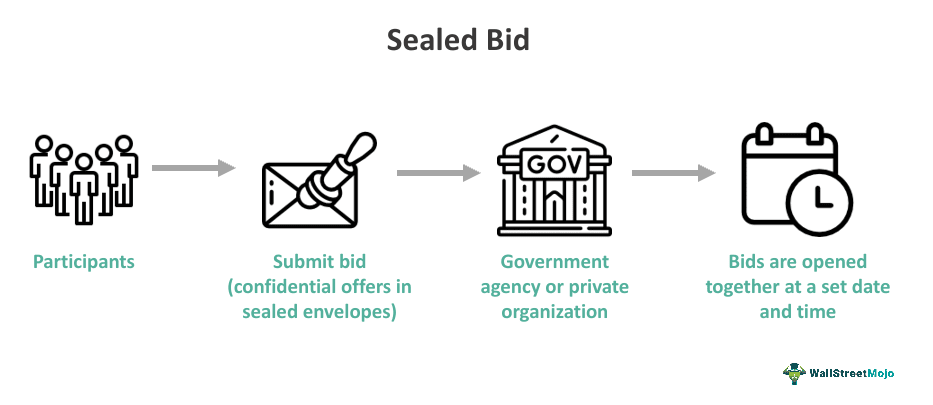
Sealed bids are a competitive bidding method where contractors submit their bids in sealed envelopes. These envelopes or electronic files submitted to an online portal stay unopened until a predetermined date and time when they are all opened together in a formal setting. This method guarantees confidentiality, as bidders are unaware of the contents of competing bids until the official opening, promoting a fair and transparent process.
Competitive bid
The competitive bidding process invites multiple contractors to submit bids for a project, each with an offer for the best terms and prices. Bids are evaluated based on set criteria like cost, quality, and delivery time, ensuring the most suitable contractor is chosen. This process promotes fair competition by giving all qualified contractors an equal opportunity to win. It encourages bidders to offer their best pricing and value, leading to cost savings. It also fosters innovation as contractors present unique solutions. By ensuring transparency and fairness, competitive bidding secures high-quality outcomes and optimal project performance.
Online bid
Online bidding platforms provide centralized, accessible spaces where contractors can submit bids from anywhere, at any time, removing geographical and time constraints. This encourages a wider pool of contractors, generating fair competition and the best pricing. They streamline the bidding process by automating tasks like bid submission, tracking, and evaluation, reducing administrative burdens and accelerating decision-making. Real-time updates and notifications keep all parties informed, ensuring transparency and minimizing miscommunication.
The bidding process
There’s no fixed way of doing the bidding process. It ultimately depends on the specifics of your project. But the process typically involves the following steps:
Step 1: Bid solicitation
After an organization has decided to open the floor for bids on a particular project, it will issue an invitation for bid (IFB), a request for quotation (RFQ), or a request for proposal (RFP). While these project management terms are unique, they all serve the same purpose: to express interest in receiving bids for a project.
Interested contractors may in turn issue a request for information (RFI), a formal document requesting clarification on certain aspects of the construction project. The tender manager then prepares a more detailed package that contains all information about the job, the issuing organization, and the specific skills and services they’re looking for.
This package also includes deadlines, expectations, supporting documents, as well as a list of requirements and supplementary information potential bidders should include in their bids.
Depending on the type of bidding process the organization prefers for the project, the invitation to bid will be extended openly or to a limited number of applicants.
READ MORE: RFI, RFP, RFQ: Understanding the Differences
Step 2: Bid preparation and submission
Once the invitation has been issued, it’s up to interested parties to assemble their bid and submit it to the organization. During this time period, parties assemble to fully review the requested document and the project’s terms.
Before drafting a bid of any kind, the service provider must first make sure that they understand the property owner’s needs and have the bandwidth and capability to deliver on those terms successfully. If they determines that the project is a good fit for the deliverables and services they offer, then they can begin assembling a construction bid.
After the bid has been drafted, the bidder should take one final look at the document as a collective before sending it back to the property owner for their official review.
Step 3: Bid evaluation and selection
During the bid evaluation and screening process, the individual or organization accepting bids reviews the various bids and project proposal submissions from outside contractors. While this process can take weeks or even months, it’s important to review each submission thoroughly and carefully. After the organization reviews each bid, they will select the bidder or bidders they want to award the contract to.
Step 4: Contract negotiation
Once a vendor has been selected, they will negotiate back and forth with the hiring organization to establish the terms and conditions under which the partnership will be governed. During these negotiations, both parties may discuss the project scope and timeline, price, access to resources, client expectations, and more.
Step 5: Project delivery
The final step of the bidding and tendering process is project delivery. This phase marks the official beginning of project work and encompasses the entirety of the project life cycle.
There are several methods of project delivery in construction project management. The most common methods include:
- Design-bid-build (DBB): Also known as traditional project delivery and is the most familiar method to project owners, design-bid-build sees the owner awarding two separate contracts for design and construction. The design team helps the hiring organization develop a set of construction drawings and specifications, which will then be presented to general contractors who will bid on the project.
- Design-build (DB): In the design-build method, the owner contracts with a single provider for both the project’s design and construction. The hired contractor will take care of the project from start to completion, making this method generally faster than design-bid-build.
- Construction manager at risk (CMAR): This method involves a contruction manager acting as the property owner’s representative and overseeing the design and construction. In CMAR, design and construction are considered two separate processes. The construction manager is present in both phases, albeit playing different roles.
What types of bid processes exist?
Open tendering
In an open tendering bid process, also called competitive bidding, an organization opens the floor for bids from any party, which can come from another organization, business, or an individual. This type of bidding is highly competitive and often occurs when an organization wants to review a wide range of candidates for the construction project across a diverse talent pool at various price points.
Selective tendering
In a selective tendering bid process, the organization accepting bids preselects a few top contractors to apply. This process makes the bidding pool smaller and typically only involves service providers that have a preexisting relationship with the organization (though this is not always the case).
Negotiated tendering
In a negotiated tendering bid process, a single contractor is preselected to complete the project. The selected provider is typically a business with a notable track record in the industry or has previously established a relationship with the project owner. In this process, the contractor and the organization accepting bids go back and forth to negotiate the terms of the project and work contract.
What role do project managers play in the bidding process?
In the tendering and bidding process, project managers play either of two roles: as a tender manager or a bidding manager. Tender managers are project managers who act as representatives for the organization seeking a service provider. Bidding managers are the project managers who act as representatives for the parties interested in providing the service or product.
Free construction bid templates and examples
The key to winning a contract is a convincing bid. Many software solutions come with construction bid templates to help teams get started quickly.
Simple construction bid template by Smartsheet
Smartsheet’s simple construction bid template is easy to read and use, with clear labels on all sections.
Customizable bid form template by Procore
Procore’s construction bid template helps simplify the bidding process and is customizable to different types of construction projects.
Easy-to-fill-out construction bid template by monday
monday.com’s construction bid template has all the important parts you need to come up with an effective bid.
FAQs
Bottom line
The bidding and tendering process helps organizations and property owners ensure that they are getting the best quality of service that they need to complete their construction project, making it a crucial part of project management.
An effective bidding process allows for a more informed decision-making, as you are provided with all necessary information to determine which contractor could offer the service that aligns with your goals. Whichever bidding process you choose to follow, it is crucial that you consider all factors that may affect the execution and the result of your project.